Majoritarian Election Systems Are Also Called
Majoritarian elections are based upon the idea that candidates. A mixed electoral system is an electoral system that combines a pluralitymajoritarian voting system with an element of proportional representation PR.

First Past The Post Electoral Reform Society Ers
In proportional systems the number of seats that each party receives in the parliaments or assemblies is.

Majoritarian election systems are also called. Majority is normally defined as 50-plus-one-vote. Most mixed systems however are mixed member majoritarian or parallel voting systems where the outcomes of the two parts of the election are separate and added together. First it is necessary to distinguish between these two types of electoral systems.
Some majoritarian systems only require a candidate to win more votes than others. In an absolute majority system the. The system applied three different modes of distribution of seats majority at the Senate proportional in the Camera proportional recovery in the Senate and for this reason was also called Minotaur as the mythological monster part man and part bull.
Instant Run-off Voting and the two round system. Also called a lobby. Plurality-at-large voting also known as block vote or multiple non-transferable vote MNTV 1 is a non-proportional voting system for electing several representatives from a single multimember electoral district using a series of check boxes and tallying votes similar to a plurality electionMultiple winners are elected simultaneously to serve the district.
The majoritarian system is also the simplest electoral system for election authorities to administer it and for voters to understand it. In a majoritarian system also known as a winner-take-all system or a first-past-the-post system the country is divided up into districts. Electoral systems the set of rules that regulate competition between parties andor candidates during elections that decide how vote shares map to seats in parliament and indeed how the electorate express their preferences have traditionally fallen into two categories.
In fact the vast majority of countries that have engaged in electoral system reform over the last few decades have adopted this method. Single-Member Majoritarian Systems In contrast to the systems just described single-member majoritarian systems seek to ensure that the winning candidate has the support of an absolute majority of the voters in his or her district. The Commonwealth House of Representatives uses a majoritarian electoral system.
At a very high level there are two basic options. Also called second ballot systems majority electoral systems attempt to provide for a greater degree of representativeness by requiring that candidates achieve a majority of votes in order to win. These are 1 absolute majority and 2 plurality systems.
A majoritarian voting system is an electoral system which gives the right to appoint all the representatives to the majority of the electors denying representation to all minorities. The council also looks to the citys. The two main variants of the former are party-list systems and the single transferable vote STV.
In some countries the majoritarian and proportional systems are combined into what are called mixed-member proportional or additional-members systems. The majoritarian system allows voters to not only choose parties but also individual candidates. A majoritarian electoral system is one in which the candidates or parties that receive most votes win2.
Majority is generally equated with democracy. We currently have an at-large election system. If an at-large election is called to choose a single candidate.
Votes are cast to individuals two round Preferences are ran. Majoritarian which include Single Member Plurality or First-Past-The-Post the Two-Round System and Alternative Vote. When electing a group of people such as a congress council or committee you need to decide which philosophy of representation that you would like to use.
Absolute majority electoral processes are designed to retain the views of the majority. The candidate who receives the highest vote share wins the election and represents the district. Broadly speaking electoral systems tend to be proportional or majoritarian.
In Australia majority systems are sometimes called preferential systems Haywood argues that one of the main disadvantages of majority electoral systems being implemented is the limited spread of representation. The pluralitymajoritarian component is usually first-past-the-post voting FPTP whereas the proportional component is most often based on party list PR. The three main variants of the latter are plurality majoritarian and so-called semiproportional systems.
Politicians then compete for individual district seats. The thing about city councilors who are also called. Thus it is better in establishing direct association between candidates and voters.
The main two types of majoritarian syst. An organized group of individuals that seeks to influence public policy. Proportional representation or majoritarian representation.
These are the main variants that today are still adopted in a few cases in the world both for selecting representatives in legislatures at the national level and for lower tiers of government. Cumulative vote block vote single non-transferable vote limited vote. Although there are a number of variants all mixed-member proportional systems elect some representatives by proportional representation and the remainder by a nonproportional formula.
Single-Member Majoritarian Systems In contrast to the systems just described single-member majoritarian systems seek to ensure that the winning candidate has the support of an absolute majority of the voters in his or her district. There are two types of majoritarian system. As noted by Aziri and Saliaj 2013 a worldwide survey found that 91 out of 191 countries use majoritarian systems.

Alternative Vote Electoral Reform Society Ers
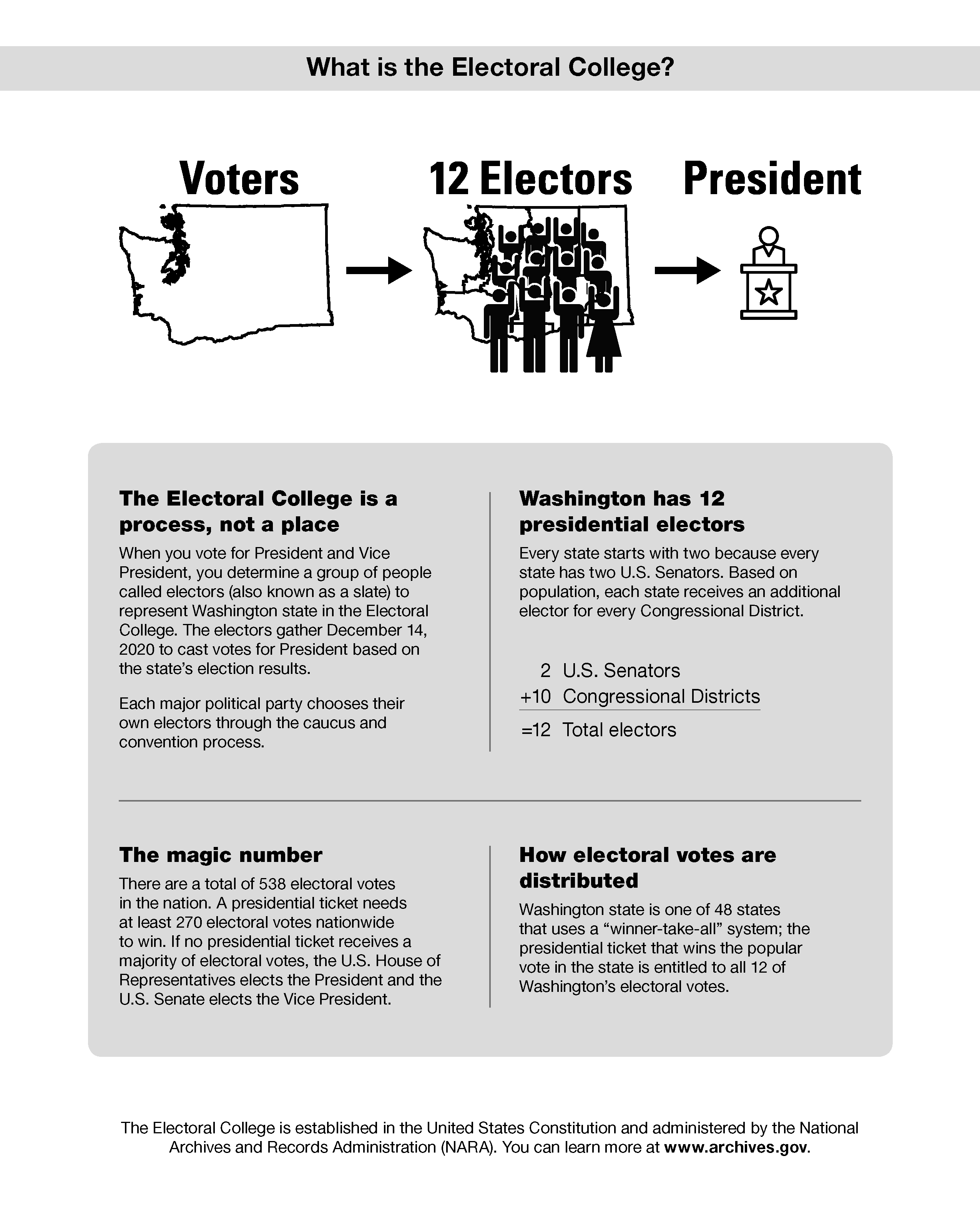
Electoral College Elections Voting Wa Secretary Of State

Election Plurality And Majority Systems Britannica
Proportional Ranked Choice Voting Example Fairvote

Election Plurality And Majority Systems Britannica

Electoral System Political Science Britannica
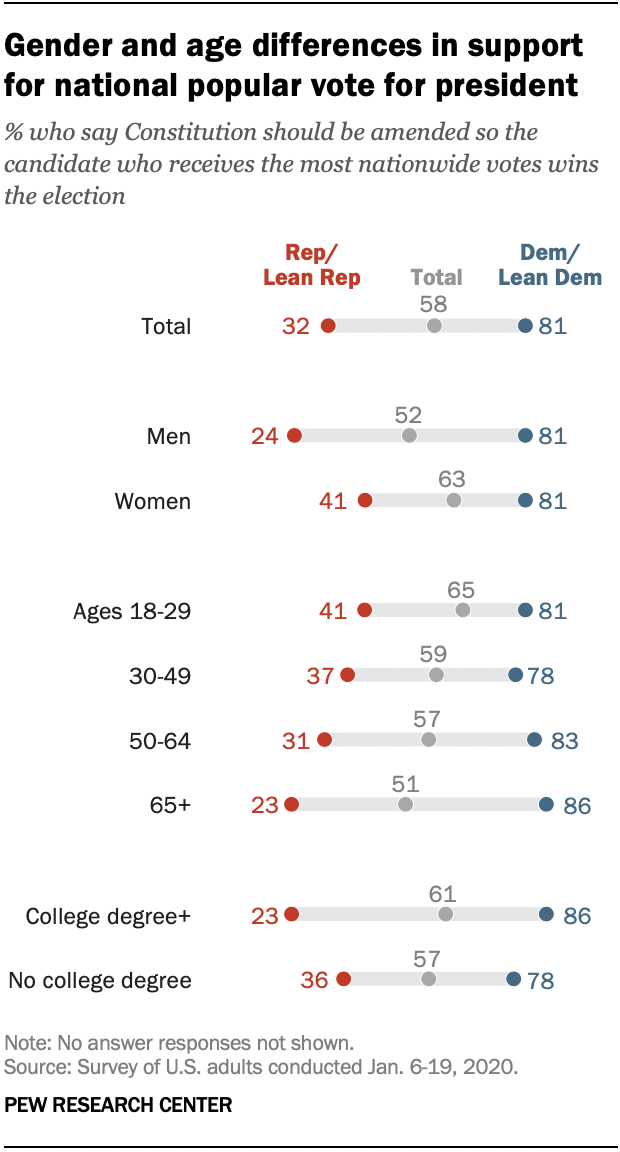
Ahead Of 2020 Election Majority Of Americans Say Popular Vote Should Replace Electoral College Pew Research Center

Advantages Disadvantages Of Proportional Representation
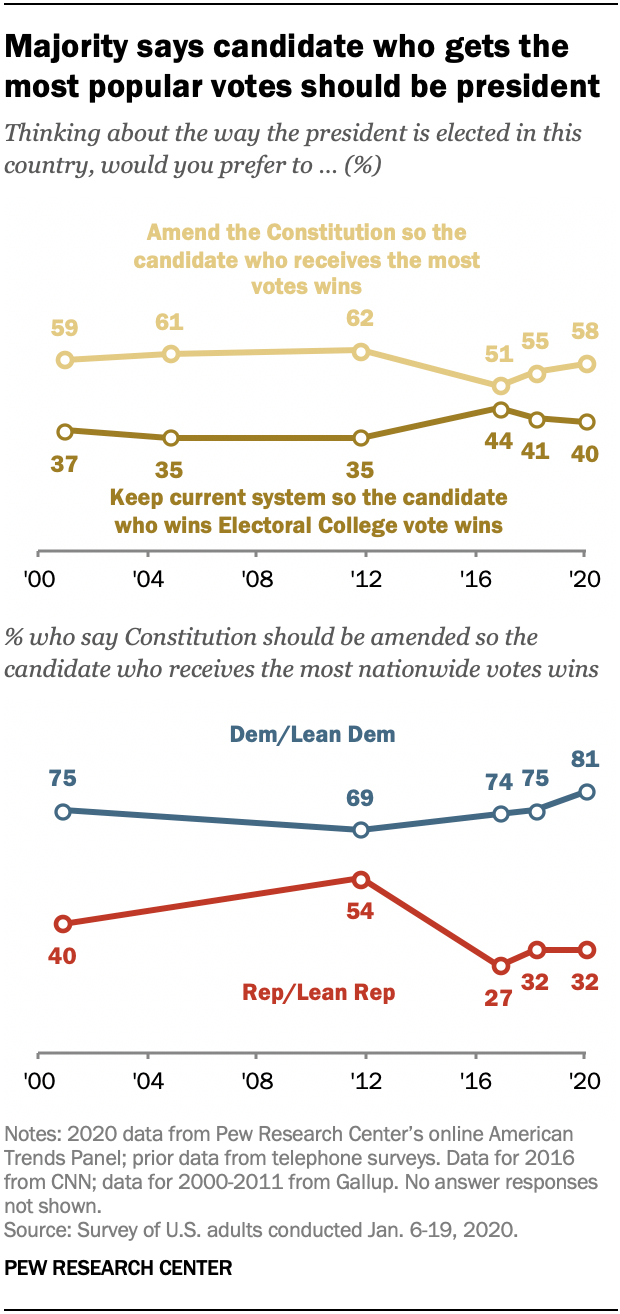
Ahead Of 2020 Election Majority Of Americans Say Popular Vote Should Replace Electoral College Pew Research Center

What Is The Mmp Voting System New Zealand Parliament

Quotations About Democracy Civiced Org
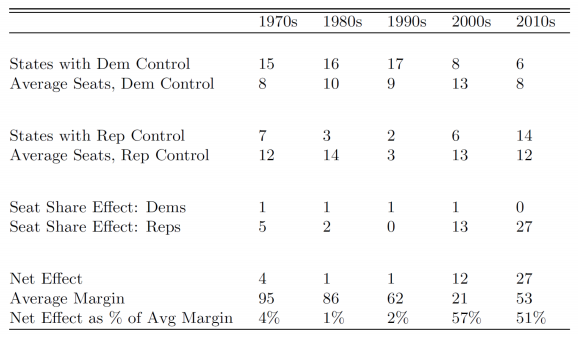
Majoritarian Versus Proportional Representation Voting Economics For Inclusive Prosperity

Election Plurality And Majority Systems Britannica

Majority Vs Plurality What Their Differences Mean For This Election Dictionary Com

Understanding America S Electoral College Infographic June 25 U S Embassy In Georgia
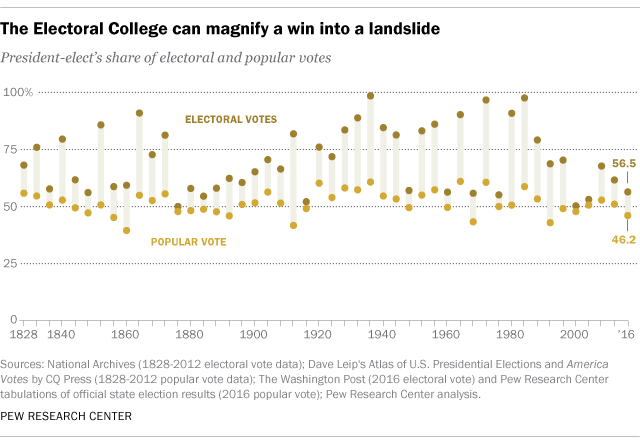
Why Electoral College Wins Are Bigger Than Popular Vote Ones Pew Research Center
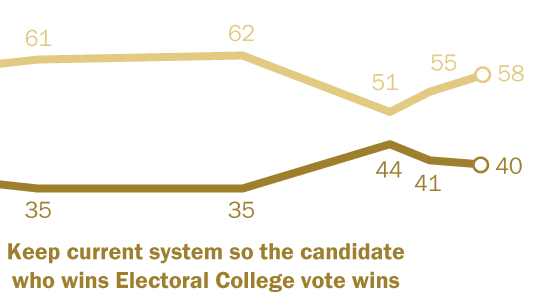
Ahead Of 2020 Election Majority Of Americans Say Popular Vote Should Replace Electoral College Pew Research Center



Post a Comment for "Majoritarian Election Systems Are Also Called"